


Advancing the frontiers of genomics
Advancing the frontiers of genomics
Advancing the frontiers of genomics
Advancing the frontiers of genomics
About Us
HanLab is a Bioinformatics and Computational Genetics group at Seoul National University College of Medicine led by Buhm Han.
Our research focuses on developing novel algorithms and software packages that contribute to the genomics and bioinformatics research communities.
We apply techniques from Computer Science, Statistics, and Bioinformatics to develop methods that enhance our understanding of the relationship between genetic variation and traits.
Our lab actively collaborates with clinicians in the Seoul National University Hospital.
HanLab members and alumni are involved in many Bioinformatics training opportunities, which are aimed at advancing interdisciplinary research skills.
Graduate students can pursue Ph.D. in the Department of Biomedical Sciences in Seoul National University College of Medicine, or M.S. or Ph.D. in the Interdisciplinary Program of Bioengineering in Seoul National University.
Research Interests
to better diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
Deep Learning
Machine Learning
Deep learning algorithm to solve problems in genomic analysis
Statistical method
Statistical method for genetic association studies
HLA imputation
Inference on alleles for highly polymorphic region in human genome
Meta-analysis
Increase statistical power by aggregating results from multiple studies
Clinical heterogeneity
Identify genetic difference in heterogeneous samples
Mendelian Randomization
Causal inference without randomized controlled trial
NGS & Cancer Genomics
Analysis on Next Generation Sequencing data
Precision medicine
Genetic understanding of a disease leads to personalized medicine
Recent Publication
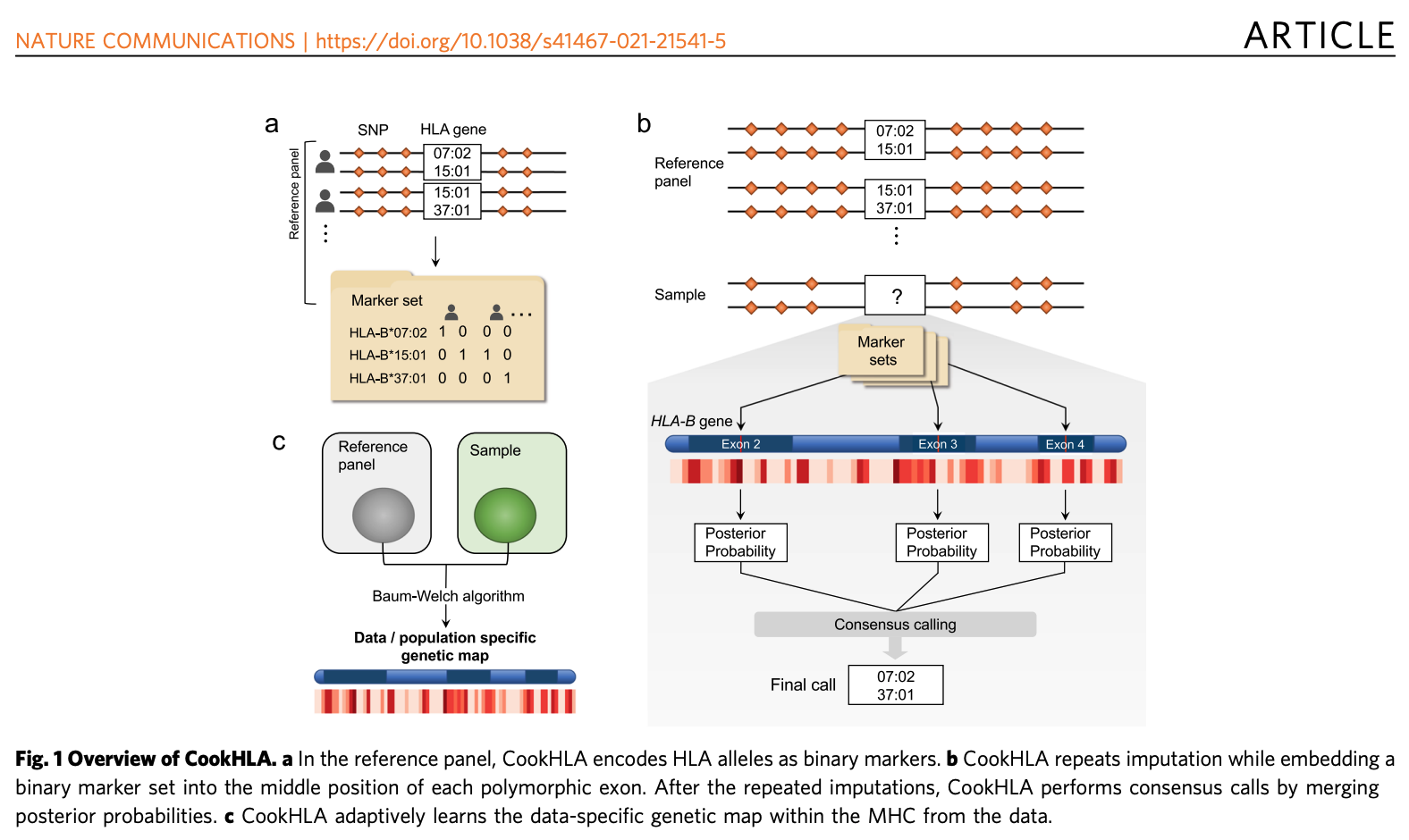
Cook, S., Choi, W., Lim, H. et al. Nat Commun 12, 1264 (2021).
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21541-5
Accurate imputation of human leukocyte antigens with CookHLA
CookHLA substantially improved imputation accuracy over previous methods, including the predecessor SNP2HLA by implementing several changes.
First, to increase accuracy and efficiency, we employed the recently released hidden Markov model (Beagle v4 and v5). Second, to further improve accuracy, we developed a procedure that can account for local variability in the exons of HLA genes. Highly polymorphic exons (exon 2/3/4 in Class I and 2/3 in Class II) are critical regions whose sequences can determine most of the 4-digit alleles. In our method, we repeat imputation by putting the marker set locally in each of the highly polymorphic exons, and use consensus posterior probabilities from the repeated analyses for final predictions (Figure B). Third, to increase accuracy even further, we adaptively learn the genetic map of MHC from the data. This map information allows us to account for the data-specific LD structure within MHC, which improves the imputation accuracy compared to the use of publicly available genetic maps (Figure C).
About Us
HanLab is a Bioinformatics and Computational Genetics group at Seoul National University College of Medicine led by Buhm Han.
Our research focuses on developing novel algorithms and software packages that contribute to the genomics and bioinformatics research communities.
We apply techniques from Computer Science, Statistics, and Bioinformatics to develop methods that enhance our understanding of the relationship between genetic variation and traits.
Our lab actively collaborates with clinicians in the Seoul National University Hospital.
Recent Publication
PLEIO (Pleiotropic Locus Exploration and Interpretation using Optimal test) : a…
CookHLA : an accurate and efficient HLA imputation method. Human leukocyte antigen…
Genomic GPS: using genetic distance from individuals to public data for…
BUHMBOX: A method to decipher pleiotropy by detecting underlying heterogeneity driven…
Seoul National University. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED

